Opening a restaurant in India involves more than just the location and menu development. Prior to serving guests, owners need to obtain necessary licenses and approvals. Permits from the central, state, and municipal governments are required for health, fire, food, and municipal regulations.
Every restaurant license in India carries its own process, documents, and timeline, making preparation crucial. Here is the complete checklist of the licenses and permits that are all going to help prevent any holdup in opening and ensure the restaurants run with confidence on day one.
Table of Contents
FSSAI Food License for Restaurants & Cafes

Every food business operator (FBO) in India is required to obtain an FSSAI restaurant license. Every FBO includes restaurants, cloud kitchens, and catering businesses. The FSSAI license secures compliance with the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 and forms a crucial part of the restaurant business setup. Displaying the 14-digit license number on premises and invoices is mandatory.
Issuing Authority: The Central license is issued by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, the State License is issued by state authorities, and Basic Registration is managed by the FoSCoS portal for small operators.
Application Process: You must register on the FoSCoS portal, upload documents, pay charges, and, if required, undergo inspection to complete the FSSAI license apply process.
Cost: Rs. 100 annually for basic registration, Rs. 2000 to Rs. 5000 annually for a state licence, and Rs. 7500 annually for a central licence.
Time: 7-10 days for basic registration, 15-30 days for a state licence, and 30-60 days for a central licence.
Validity: 1 to 5 years.
Health and Trade License for Food Establishments

Municipal corporations in India grant a Health and Trade License to restaurants, cafes, and street food vendors. The license certifies that there is adherence to sanitation and public health standards.
Issuing Authority: Municipal corporations like MCD for Delhi, NDMC for central Delhi, and BBMP for Bangalore.
Application Process: Apply at the local municipal portal or zonal office, submit documents, and pay fees.
Cost: Fees vary by city and seating capacity. For example, NDMC charges Rs. 5000 per year for outlets with up to 50 seats and Rs. 10,000 per year for larger outlets.
Processing Time: Up to 30 days.
Validity: Renewed annually with resubmission of documents and fees.
Shop and Establishment Act Registration for Restaurants
The Shop and Establishment License contains legislation on employee entitlements, working hours, and health and safety in any establishment. All restaurants that operate in a particular state must be registered under the respective state's Shop and Establishment Act.
Authority Issuing: The State's Department of Labour.
Application Process: Fill out the online application form located on the Labour Department website or go to your municipality.
Cost: Varies with states and the number of employees.
Processing Time: Approximately 30 days.
Validity: Ranges from five years to a lifetime period, depending on the state.
GST Registration for Restaurants
If your restaurant's turnover exceeds the limit, you should complete the restaurant GST registration. This GST registration allows restaurants to collect tax consistently and claim an input credit.
Issuing Authority: Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
Application Process: Enter details via the GST portal, provide identity, bank, and business proof, and obtain a GSTIN after verification through GST registration online.
Costs: Free on the portal, although consultants may charge from Rs. 1000 up to Rs. 8000.
Processing Time: Usually 2-7 working days.
Validity: Permanent unless cancelled. Though monthly or quarterly returns must be filed.
Eating House License for Restaurant Dining
Restaurants serving food and beverages for public dining must hold an Eating House License.
Issuing Authority: The local or state Police Commissioner in charge of Licensing.
Application Process: Create an account on the police licensing portal, submit the required documents, and participate in an in-person verification.
Cost: Approximately Rs. 300 for a license, which lasts up to 3 years.
Processing Time: 45-60 days.
Validity: Generally, 3 years with renewal necessary.
Fire Safety NOC for Restaurant Premises

Restaurants need to establish compliance with fire safety standards according to the National Building Code.
Issuing Authority: State Fire Services Department
Application Process: Provide building plans, layouts, and details of fire systems. Inspections are conducted prior to approval.
Cost: Typically free.
Processing Time: 25-35 working days.
Validity: Generally, 3 years.
Environmental Clearance License for Restaurants

Food establishments producing wastewater, grease-laden effluents, or using diesel generators will require an Environmental Clearance License. Restaurant license in India that operates under an Environmental Clearance License, permitting the restaurant to operate following environmental and pollution controls.
Issuing Authority: The Ministry of Environment and Forests reviews the EIA state and grants clearance.
Application Process: Carry out an EIA study, submit the EIA along with a detailed questionnaire as the final application, and receive approval from the ministry.
Processing Time: Generally issued within 105 days from the Final EIA report acceptance date.
Validity: Validity period may last from five years to thirty years, depending on the category of the project.
Liquor License for Serving Alcoholic Beverages
A restaurant wishing to serve alcoholic beverages must obtain a Liquor License. Selling liquor without permission is against the law and carries hefty penalties.
Issuing Authority: State Excise Departments.
Application Process: File the application with the state excise office as per local rules.
Cost: State and specific to the establishment. It is usually Rs. 1,50,000 a year for restaurants as a starting point.
Processing Time: 30-60 days.
Validity: Generally valid for one year and should be renewed every year.
Music License for Restaurants and Cafes
Restaurants that play copyrighted music have to get a Music License. So composers and producers are paid their royalties.
Issuing Authority: PPL is the one that handles the recorded music, while IPRS handles live or public performances.
Application Process: You are expected to apply through the official portals of PPL or IPRS, fill in the information about the business and the venue, and then pay the respective fees.
Cost: Generally Rs. 5000 to Rs. 10,000 or more based on location and venue.
Processing Time: 7-10 working days.
Validity: One-year license for annual renewal.
Signage License and Display Permits for Restaurants
Restaurants displaying outdoor signs, boards, or banners need to have a Signage License. This is one of the key permits required to open a restaurant, ensuring that visibility and marketing efforts comply with local regulations while avoiding penalties or disputes.
Issuing Authority: Local municipal corporations.
Application Process: Apply at the municipal office with signed details.
Cost: Fees vary according to city, sign type, and size.
Processing Time: Around 30 days.
Validity: Usually one year.
Additional Permissions for Restaurant Operations
Any restaurant might need additional approvals
- Registration with delivery aggregators like Swiggy or Zomato.
- Municipal clearance for outdoor seating.
- Waste disposal contracts with approved vendors.
- Pest control certification in risk areas.
Key Compliance Practices for Restaurants
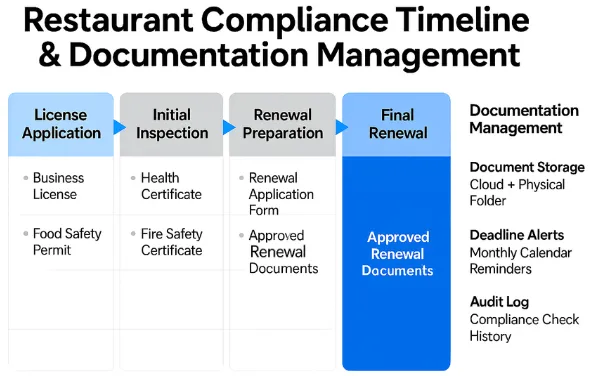
- Start early since approvals take weeks.
- Seek local authorities or rules applicable in the city.
- Have documents in place, such as site plans and NOCs.
- Ensure hygiene standards for employees and kitchen operations.
- Track document renewal dates for all licenses.
Restaurant Regulatory Compliance: Final Words
In order for your restaurant to be operated in a decent way and in accordance with the law, all the permits and license required for restaurant, as well as all the compliance steps, need to be maintained.
Being organised, following safety and hygiene standards, doing MSME Registration online, and holding renewal records go a long way to prevent the occurrence of fines and win the trust of the customers. Proper business organisation sets the basis of a successful and sustainable restaurant industry in India.






