Starting a pharmacy is one of the safest and most lucrative ventures in the healthcare industry. Drugs are always in demand, and with the rise of hospitals, clinics, and private healthcare facilities, the demand for pharmacies keeps increasing. Most entrepreneurs find it a viable option despite requiring initial capital investment, as it provides a guaranteed income and significant scope for expansion. However, starting a pharmacy by simply renting out a shop and selling medicines is not straightforward.
There are stringent norms to follow, infrastructure specifications to be adhered to, and important licenses that need to be acquired to open a medical store in India. This comprehensive guide outlines the types of medical stores you may set up, the licenses you must have, all the documents required for the establishment, and proven tips for successfully setting up a pharmacy business in India.
Table of Contents
Types of Medical Stores You Can Open
Before a pharmacy is commenced, the type of pharmacy needs to be established because it influences the setup expense, location, and personnel requirements.
1. Hospital Pharmacy: This pharmacy exists within a hospital building and dispenses drugs to patients admitted to that hospital or visitors of that facility. These are typically operated by healthcare institutions themselves.
2. Independent Pharmacy: This is the most common type of pharmacy store, and it is usually located in residential areas or standalone commercial spaces. It is small to medium-sized, handling day-to-day medicine requirements for the local community.
3. Franchise Shop or Chain Pharmacy: A portion of a larger brand, mostly located in malls or crowded commercial markets. These operate under established brand guidelines and protocols.
4. Township Medical Store: Installed in towns or villages to serve the inhabitants. These cater to semi-urban and rural healthcare needs.
5. Government-Approved Pharmacy: Operated under government schemes or policies, mostly in government premises or healthcare centers.
Partners or individuals mostly own townships and independent shops, whereas hospitals and chain pharmacies are mostly operated by large healthcare companies and corporations.
Space and Storage Requirements
The law imposes strict rules when it comes to pharmacy shop size and storage infrastructure. A retail pharmacy must occupy at least 10 square meters, while a wholesale pharmacy must occupy 15 square meters or more. Storage is another crucial aspect because some medicines like vaccines, insulin, and sera must be stored in a refrigerator to maintain potency. The shop thus must have a working air conditioner or fridge to meet pharmacy regulations in India and ensure proper drug preservation and compliance with pharmaceutical standards.
Staff Requirements
Pharmacies cannot run without competent personnel. For retail pharmacies, during working hours, a registered pharmacist is required to be present at all times to dispense medicines and provide professional guidance. For wholesale pharmacies, sales can be permitted with the supervision of an experienced pharmacist who has either one year of relevant experience or four years of pharmacy experience approved by the Drug Control Department.
Business Registration Options
The next step is pharmacy business registration India. The type of structure you choose will determine how your company will be taxed and controlled legally.
- Sole Proprietorship: It is owned by an individual, easy to set up, and a PAN card and bank account are the primary requirements. This is the most common choice for small pharmacies.
- Partnership Firm: It is owned by two or more individuals and needs to be registered with the Registrar of Firms. This structure allows shared responsibility and investment.
- One Person Company (OPC): A single person can avail company benefits such as limited liability without the complexity of a full private company. Registered with the Registrar of Companies.
- Private Limited Company: Requires two or more members and directors, but not the public, to purchase shares. Suitable for larger pharmacy chains and operations.
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): A mix of a partnership and company benefit providing both flexibility and liability protection. Registered with the Registrar of Companies.
All these have their own advantages and disadvantages. Proprietorship and partnership are typical for smaller independent pharmacies. Larger chains prefer private limited or LLP structures for liability protection and scaling.
Licenses and Drug Registration Needed
It requires more than a business registration to run a pharmacy legally. Several critical licenses must be obtained:
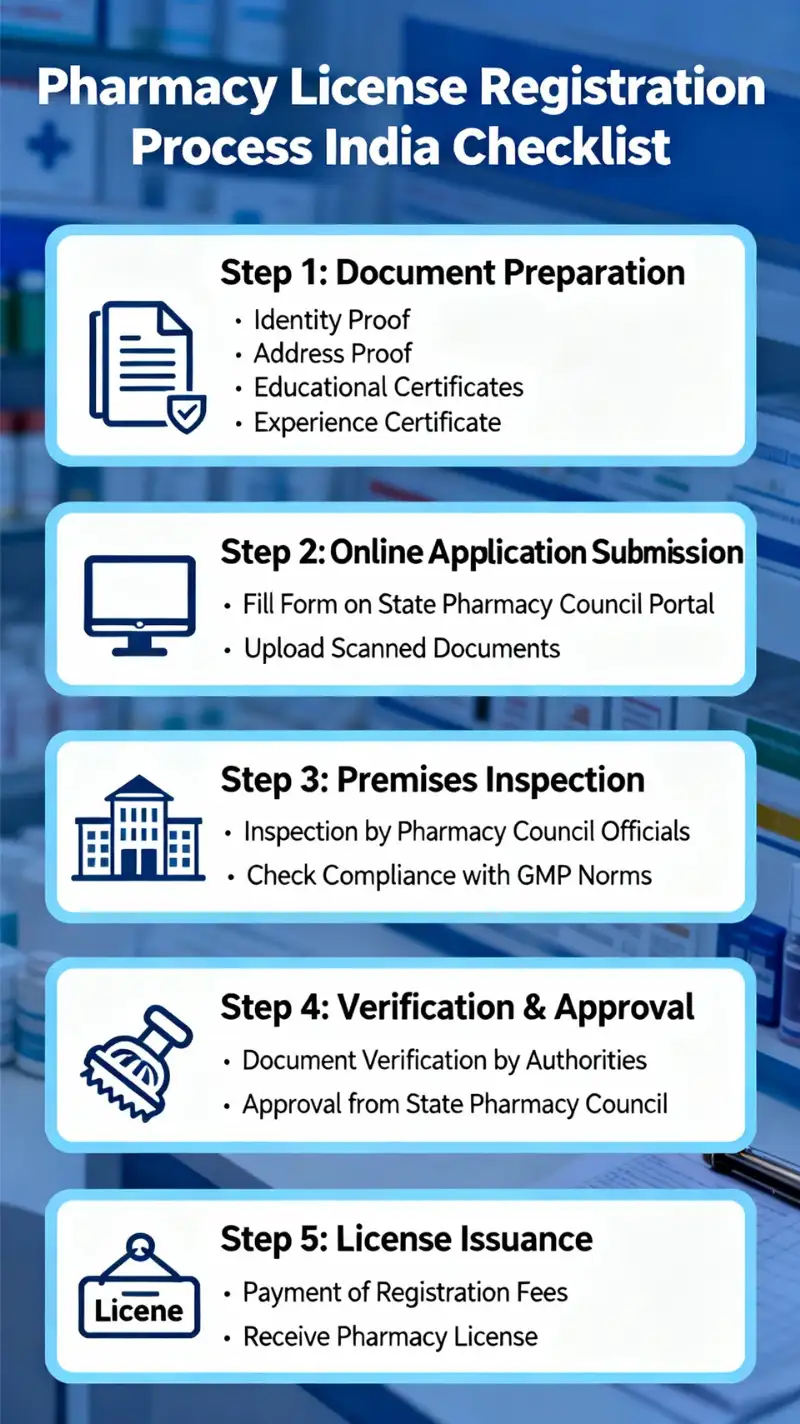
1. Pharmacy License
The most crucial license is obtaining a pharmacy license in India. It can only be awarded to licensed pharmacists who have a B.Pharm (Bachelor of Pharmacy) or M.Pharm (Master of Pharmacy) degree. You cannot legally sell drugs without a valid pharmacy license from your state pharmacy council. This license certifies that a qualified pharmacist is responsible for the pharmacy operations.
2. Drug License
All medical stores must possess a drug license for pharmacy prior to conducting any operations. This is awarded by the Central Drugs Standards Control Organization (CDSCO) and the State Drugs Control Organization. The drug license is of two types:
- Retail Drug License for Medical Store: Required for chemist stores that sell medicines directly to consumers. This is the most common type for standalone pharmacies.
- Wholesale Drug License: Required for wholesale dealers who supply medicines to other retail pharmacies, hospitals, or clinics.
3. Shop and Establishment Registration
Shop and Establishment Registration is required by all shops under the act of their respective states. It helps with compliance with local working and operational rules, labor laws, and shop timings. This registration varies by state but is mandatory for legal operation.
4. GST Registration
If your pharmacy's turnover is above the threshold limit in a year, you must apply for GST registration. The threshold is ₹40 lakhs in regular states and ₹20 lakhs in special category states. GST registration online is mandatory for larger operations and helps with proper tax compliance and invoicing.
Budget Needed to Open a Medical Store
In every region, the cost of opening a pharmacy varies depending on the size of the store and the appropriate type of business structure. Typically, a small standalone pharmacy needs an amount ranging from ₹5 to ₹10 lakhs to cover rent for 3-6 months, furniture and fixtures, storage equipment, refrigeration units, licensing fees, initial inventory of medicines, and working capital. For franchises or established chain pharmacies, the investment is higher and can range anywhere from ₹20 to ₹30 lakhs or more, depending on the brand's standards and location.
This investment typically breaks down as:
- Shop rent deposit and 3-6 months advance: ₹2-3 lakhs
- Furniture, shelving, and fixtures: ₹1-1.5 lakhs
- Refrigeration and storage equipment: ₹50,000-₹1 lakh
- Licensing and registration fees: ₹25,000-₹50,000
- Initial inventory of medicines: ₹1.5-2 lakhs
- POS system and billing software: ₹30,000-₹50,000
- Working capital and contingency: ₹50,000-₹1 lakh
Key Steps for Running a Pharmacy Successfully
- Pick a Suitable Location: Localities with residential crowds, areas along clinics, or locations near hospital campuses draw regular customers and ensure consistent footfall. High visibility and accessibility are crucial.
- Keep Records in Order: Maintain proper purchase and sale invoices to meet audits and regulatory requirements. Digital record-keeping is increasingly important for compliance.
- Stay Updated: Always renew your drug license for pharmacy and shop registration licenses before expiration. Set reminders for license renewal dates to avoid legal complications.
- Train Your Employees: Trained pharmacists and healthcare professionals facilitate smooth transactions and build customer confidence. Invest in staff training and development.
- Implement Technology: Latest billing systems and stock management tools make controlling inventory more efficient and reduce medication wastage and errors.
- Maintain Cleanliness and Organization: A clean, well-organized pharmacy inspires customer confidence and ensures regulatory compliance with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) norms.
- Build Customer Relationships: Offer professional advice, maintain privacy for patient information, and provide accurate dosage guidance to build loyalty and reputation.
Final Words
The Indian pharmacy business continues to grow, with huge opportunities for entrepreneurs and healthcare professionals. To be able to operate successfully, each pharmacy will need to meet legal compliance requirements, acquire all required permits, and implement proper security and storage procedures. With proper planning and full compliance with regulatory requirements, a pharmacy can become a safe and lucrative business for many years.
Beginning may look intimidating, but once you've obtained your pharmacy license in India, completed business registration, and met all storage and infrastructure requirements, you will have your cornerstones set. For anyone willing to venture the effort, opening a pharmacy is at the same time a secure and viable option in the growing healthcare sector and India's expanding healthcare horizon.






